Year in Review: Top stories for 2024
January 06, 2025
Most-read website stories
Compressortech2 readers gravitated toward an eclectic mix of stories on our website in 2024. The most read stories of the year included Tech Corners about dry gas seal systems and Cornerstones of Compression articles from industry export Norm Shade.
Here’s a list of the most read news stories from our website during the past year.
McDermott wins EPCI contract for LNG Project
McDermott has been awarded an engineering, procurement, construction and installation (EPCI) contract by QatarEnergy LNG for the North Field South (NFS) Offshore Pipelines and Cables Project.
This new contract is in addition to the awards received by McDermott earlier for the NFS Pipelines FEED, the NFS Jackets EPCI, and the NFXP Topsides and Pipelines which included the NFS Topsides.
The NFS infrastructure is designed to supply feed gas for two additional LNG trains and is part of the North Field Expansion Project (NFXP), which will help increase the total LNG production in the State of Qatar from the current 77 million tons per annum (MTPA) to 142 MTPA.
The scope of the contract comprises EPCI of almost 250 kilometers of offshore and onshore gas pipelines connecting five new offshore wellhead platforms with two new onshore LNG trains in addition to subsea composite power and control cables. The project will be managed from the McDermott Doha office with in-country fabrication support from the QFAB fabrication yard, and will be installed with McDermott’s inhouse marine assets.
Enbridge, Fortis BC studying hydrogen blending
Enbridge and FortisBC Energy said they are studying how hydrogen can be safely and reliably delivered using the existing gas pipeline infrastructure in British Columbia, Canada.
This hydrogen blending study, which is being supported in part by the British Columbia Ministry of Energy, will look at the percentage of hydrogen that can be safely transported through gas pipeline infrastructure, such as Enbridge’s Westcoast natural gas transmission system, as well as FortisBC’s gas transmission and distribution systems.
If upon completion it is determined that hydrogen can be safely transported in this infrastructure, the study will be used to inform the development of codes and standards to regulate its transportation and help to inform the development of a commercial hydrogen market in the province, the companies said.
“This important study will play a critical role in determining how existing energy infrastructure can be used to transport hydrogen and how we can continue to work to advance the energy transition,” said Cynthia Hansen, Enbridge executive vice president and president, Gas Transmission and Midstream.
Enbridge’s Westcoast system operates more than 2,900 km of pipeline from the northeast of the province to the U.S.-Canada border and east to the B.C.-Alberta border. This pipeline system supplies natural gas to FortisBC’s approximately 51,000 km gas transmission and distribution system.
Atlas Copco sees growth in LNG, hydrogen applications
Giving its annual overview of the previous year, Atlas Copco said demand for equipment and services in its Compressor Technique business was strong and order volumes increased throughout the year, especially for equipment in the first half of 2023.
The Compressor Technique segment covers equipment for compression of air and gases, gas treatment equipment and related services. Stationary industrial air compressors and associated air-treatment products, spare parts and service represent about 90% of revenues. Large gas and process compressors, including related service, represent about 10%.
In total, the order intake increased 9% organically. Solid order growth was achieved for the service business with increased order volumes in all regions. The favorable order development was supported by higher demand for spare parts, repair, maintenance, and service contracts, the latter supported by an increased number of connected products in the market. The order intake for equipment increased with increased order volumes in all regions.
Orders for industrial compressors increased primarily driven by growing demand for large industrial compressors, while the demand for small and medium-sized compressors grew at a more moderate pace. The overall growth was a result of a generally favorable business environment but was also helped by solid demand from customer segments contributing to the transition to a low-carbon society, such as the production of batteries for electric cars, solar panels, LNG, and hydrogen applications. In total, order volumes increased in all regions.
The order intake for gas and process compressors increased significantly, supported, but not entirely driven by, several larger orders related to LNG and carbon capture applications in the first quarter. Order volumes increased in all regions, most notably in North America and Asia
EPA approves Piñon CO2 sequestration plan
Piñon Midstream received approval from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for its monitoring, reporting and verification plan for the permanent sequestration of carbon dioxide in its two acid gas injection (AGI) wells at Piñon’s Dark Horse Treating Facility in Lea County, New Mexico.

Piñon said its Dark Horse Treating Facility is the largest AGI system that is currently permitted and operating in the state of New Mexico. Both of Piñon’s AGI wells—Independence AGI #1 and Independence AGI #2—are Devonian wells, reaching depths of approximately 18,000 ft. below the surface into rock formations located several thousand feet below water aquifers and existing Delaware Basin oil and natural gas producing formations.
The two AGI wells are permitted for a combined 20 million cubic feet per day (20 MMcf/d) of CO2 and hydrogen sulfide injection, which equates to ~250,000 metric tons of CO2 and ~110,000 MT of H2S annually based on current gas compositions. These two wells provide sequestration redundancy for Delaware Basin operators who use Piñon’s scalable and centralized treatment and sequestration facility to mitigate flaring and unlock valuable drilling inventory in the area.
Piñon’s approved plan, which became effective June 15, provides a full description of technical procedures for sequestration, monitoring, and verification that have been put in place at the Dark Horse Treating Facility to ensure permanent sequestration. The approved MRV plan also satisfies a major requirement for Piñon’s eligibility to receive 45Q and enhanced tax credits in accordance with the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022.
At its current operational rate, Piñon’s Dark Horse Treating Facility is projected to capture and sequester more than 190,000 MT of CO2 and 90,000 MT of H2S over the next twelve months.
Image: Pinon Midstream
First LNG at New Fortress Energy Asset

New Fortress Energy has achieved first liquefied natural gas (LNG) for its initial Fast LNG asset offshore Altamira, Mexico.
The FLNG establishes itself as the fastest large-scale LNG project ever developed, the company said in a news release.
NFE said its proprietary Fast LNG design pairs the latest advancements in modular liquefaction technology with jack up rigs or similar offshore infrastructure to enable a faster deployment schedule than traditional liquefaction facilities. The company said Fast LNG harnesses existing FLNG (floating liquefied natural gas) technology and combines it with a modular approach, allowing for scalability, affordability, and speed of natural gas liquefaction.
With a production capacity of 1.4 MTPA, or approximately 70 TBtus, the FLNG completes the vertical integration of NFE’s LNG portfolio and will play a pivotal role in supplying low-cost, clean LNG to the Company’s downstream terminal customers.
“First LNG represents a transformative moment for our Company and the industry as a whole, and reaffirms our position as a fully integrated leader in the global LNG market,” said Wes Edens, Chairman and CEO of New Fortress Energy.
Chart Industries said its Integrated Pre-Cooled Single Mixed Refrigerant (IPSMR) process technology helped deliver the first LNG at the asset.
Hydrogen fuel adoption in U.S., Europe could cost over $1 trillion
At the CERAWeek by S&P Global energy conference happening in Houston, Texas, this week, Reuters reported that a Mitsubishi Heavy Industries executive said adopting hydrogen fuel in the U.S. and Europe will require infrastructure investments in excess of US$1 trillion.
Emmanouil Kakaras, an executive vice president for Mitsubishi, said significant demand is required for a wholesale move to hydrogen, and it can only happen if there are investments in infrastructure to reduce the cost. “If you count the funding to bridge the gap, you will easily get to $1 trillion,” he said in the Reuters report.
Kakaras added that infrastructure investments in Europe would encourage wider adoption of hydrogen by 2035. When coupled with U.S. carbon capture and storage efforts, this approach could facilitate the energy transition, he said.
Both the European Union (EU) and the United States recently announced funding availabilities focused on expanding the hydrogen infrastructure.
On Feb. 15, the European Commission announced it had approved as much as 6.9 billion euros (approx. US$7.5 billion) in funding to support the growth of hydrogen infrastructure via a project called Important Project of Common European Interest (IPCEI) Hy2Infra. The funding will come from seven member states — France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal and Slovakia — and is expected to attract an additional 5.4 billion euros (approx. US$5.9 billion) in private investment.
Major LNG project launched in Philippines
What developers are calling the first expansive integrated LNG facility in the Philippines has been launched.
The US$3.3 billion project is being spearheaded by Meralco PowerGen (MGen), Aboitiz Power Corp. (AP) and San Miguel Global Power Holdings Corp. (SMGP) in the city of Batangas.
This initiative is designed to help boost energy security and steer the country towards a cleaner, more sustainable future in line with the Marcos administration’s push for more natural gas in the country’s energy mix.
In the deal, MGen and AP will jointly invest in two of SMGP’s gas-fired power plants—the 1278 MW Ilijan power plant and a new 1320 MW combined cycle power facility which is expected to start operations by the end of 2024 – and together with SMGP will invest in almost 100% of the LNG import and regasification terminal owned by Linseed Field Corp.
Additionally, all three companies will acquire the LNG import and regasification terminal of Linseed Field Corp. This will be used to receive, store and process LNG fuel for the two power plants, thus fully integrating the local energy sector into the global natural gas supply chain.
The collaboration will substantially augment the country’s power supply with over 2500 MW of generation capacity once fully operational, backed by advanced LNG storage and regasification capabilities. This effort will not only meet the country’s energy requirements but also support its environmental objectives by significantly lowering emissions, the companies said.
Neuman & Esser leading hydrogen project

Neuman & Esser will be in charge of building a hydrogen plant for Chile’s National Petroleum Co. (Enap) with production projected to start in 2025.
In January 2023, the company announced the start of its own green hydrogen project in the Cabo Negro complex, in Magallanes. The plant will be powered by the Vientos Patagónico wind farm – of which Enap is the majority shareholder – and will have a capacity of 1 MW, which will be used for vehicle charging stations and to power the furnace of the plant.
With the construction of this plant, Enap hopes to generate knowledge and experience in the production and use of this energy in the Magallanes region, as part of its strategy for the development of new fuels.
Neuman & Esser was awarded the bidding process for the project, which considers electrolysis, storage, a charging station and a detailed training plan for company workers, among others.
Abu Dhabi’s national oil company buys into U.S. hydrogen project
ADNOC will acquire a 35% equity stake in Exxon Mobil’s proposed low-carbon hydrogen and ammonia production facility in Baytown, Texas.
Contingent on supportive government policy and necessary regulatory permits, the facility is expected to be the world’s largest of its kind upon startup, capable of producing up to 1 billion cubic feet (bcf) daily of low-carbon hydrogen, which is virtually carbon-free with approximately 98% of carbon dioxide (CO2) removed and more than 1 million tons of low-carbon ammonia per year. A final investment decision (FID) is expected in 2025 with anticipated startup in 2029.
“This strategic investment is a significant step for ADNOC as we grow our portfolio of lower-carbon energy sources and deliver on our international growth strategy,” said Sultan Ahmed Al Jaber, minister of Industry and Advanced Technology and ADNOC Managing Director and Group CEO. “We look forward to partnering with ExxonMobil on this low carbon-intensity and technologically advanced project to meet rising demand and help decarbonize heavy-emitting sectors.”
Terms were not released.
Following FID for the project, ADNOC intends to support ongoing community initiatives in the Baytown area, in line with the company’s commitment to sustainability and education in the locations where it operates. This commitment reflects ADNOC’s broader strategy to foster community development and ensure that the benefits of its projects extend beyond environmental gains to include social and economic advancements.
Cedar LNG project orders announced
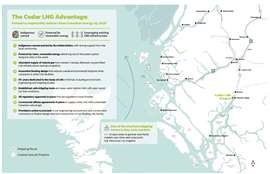
Baker Hughes will supply Cedar LNG in Canada with electric-driven liquefaction technologies.
Baker Hughes will supply a range of turbomachinery equipment, including four electric-driven main refrigeration compressors, two electric-driven boil-off gas compressors and six centrifugal pumps. Powered by renewable electricity, Cedar LNG will be one of the lowest carbon intensity LNG facilities in the world, the company said.
The order comes from Black & Veatch, the engineering, construction and consulting leader for the Cedar LNG project, which brings together the Haisla Nation and Pembina Pipeline Corporation (Pembina) to develop the Haisla Nation-led project. The project is a key element of the Haisla Nation’s economic and social development strategy and will further advance reconciliation by allowing the Haisla Nation, for the first time ever, to directly own and participate in a major industrial development in its territory. Today, the Haisla people are centered on Kitamaat Village. Home to approximately 700 of the 2,023+ Haisla membership, Kitamaat Village sits at the head of the Douglas Channel in British Columbia, Canada.
“This award is the latest important milestone for Baker Hughes in the LNG market, demonstrating the strength of our portfolio and our commitment to collaborating with industry partners while providing efficient and lower carbon solutions for the natural gas market,” said Ganesh Ramaswamy, executive vice president of Industrial & Energy Technology at Baker Hughes. “Over the next decade, electrification will play a critical role in the energy transition, enabling further reduction of carbon emissions from natural gas.”
MAGAZINE
NEWSLETTER

CONNECT WITH THE TEAM







