NGL Production Continues Record Pace
March 22, 2019
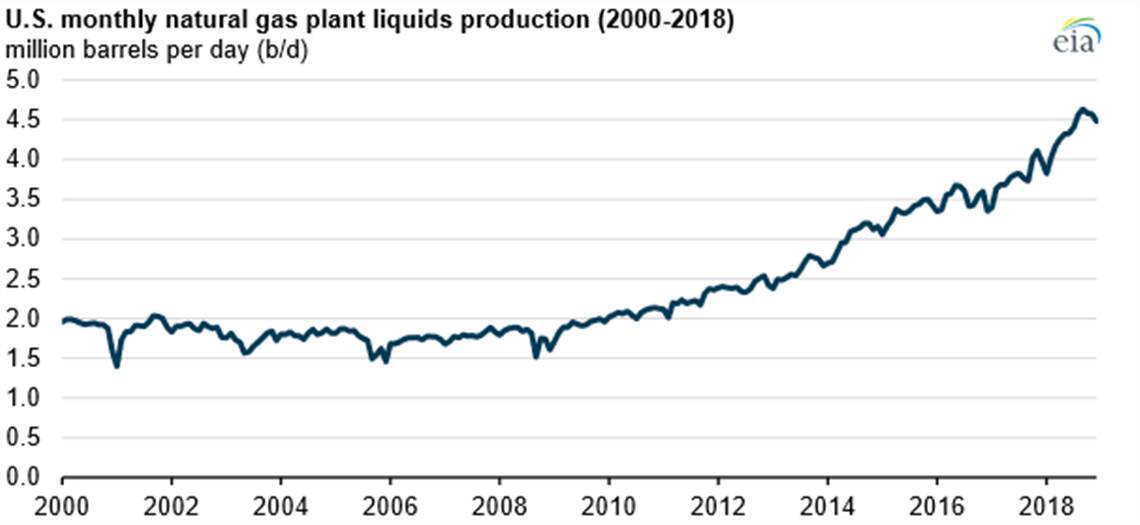
Since 2012, when horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing techniques became more common, U.S. production of natural gas plant liquids (NGL) has significantly increased, averaging 4.3 million barrels per day (b/d) in 2018, up from 2.5 million b/d in 2012, according to a new report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA).
The Permian, Eagle Ford, and Appalachian regions made up more than half of all U.S. NGL production in 2017. An additional one-quarter of NGL production was located in three other regions—the Anadarko Basin in western Oklahoma and Texas; the Bakken play in North Dakota and eastern Montana; and the Green River, Piceance, Uinta, and Paradox Basins in the Western Rockies region of Utah, Wyoming, and Colorado.
 Wet natural gas includes methane—the primary component of delivered natural gas—as well as NGLs such as ethane, propane, normal butane, isobutane and natural gasoline. Once impurities such as water, hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide are removed from the wet gas, the mixed NGLs are transported for further processing at fractionation plants that separate the NGLs into distinct commodities, while methane is shipped via pipelines.
Wet natural gas includes methane—the primary component of delivered natural gas—as well as NGLs such as ethane, propane, normal butane, isobutane and natural gasoline. Once impurities such as water, hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide are removed from the wet gas, the mixed NGLs are transported for further processing at fractionation plants that separate the NGLs into distinct commodities, while methane is shipped via pipelines.
NGLs typically sell at higher values than methane on a heat-content basis because they are priced against crude oil-derived fuels. The yield of these liquid products can vary depending on the constitution of the raw natural gas, the technology used to extract NGLs at processing plants, and the NGPL market prices and demand, especially for ethane. The domestic and international markets for individual NGL products have grown with the growing U.S. NGL production, as these liquids are used for feedstock in manufacturing plastics and resins.
NGL production has generally increased across all regions since 2012 as production of natural gas has grown. The largest increase has been in the Northern Appalachian region, where production increased from 43 thousand b/d in 2012 to 512 thousand b/d in 2017. NGPL production has doubled in both the Permian Basin in western Texas and southeastern New Mexico and the Eagle Ford play in southern Texas from 2012 to 2017. NGPL production in the Bakken play more than tripled.
 In most production regions, NGLs must be shipped by pipeline to fractionation centers, such as Mont Belvieu, Texas, and Conway, Kan., both of which act as storage, distribution, and pricing hubs for NGLs. Northern Appalachia is one of the few areas that fractionate NGLs in the same region where they are produced.
In most production regions, NGLs must be shipped by pipeline to fractionation centers, such as Mont Belvieu, Texas, and Conway, Kan., both of which act as storage, distribution, and pricing hubs for NGLs. Northern Appalachia is one of the few areas that fractionate NGLs in the same region where they are produced.
In 2017, the U.S. volume-weighted average yield of NGPLs from raw natural gas was 84 barrels per million cubic feet (b/MMcf) of processed natural gas. The Bakken generates the highest NGPL yield, or richest natural gas, with an average of 143 b/MMcf. Raw natural gas from the Permian and Eagle Ford yields 95 b/MMcf and 107 b/MMcf, respectively. At 31 b/MMcf, the Western Rockies raw natural gas has the lowest NGPL yield. Producers will generally prioritize production from richer formations to maximize NGPL yields unless they lack the infrastructure to process wet gas and transport the liquids to market.
MAGAZINE
NEWSLETTER
CONNECT WITH THE TEAM





